3D printing is generally known as the process of making a physical object from a 3D digital model. To bring the model to life, it lays down thin layers of an object’s material in order to turn the CAD representation into a physical form.
3D printing brings two fundamental innovations: the manipulation of objects in their digital format and the manufacturing of new shapes by the addition of material.
3D printing offers an innovative approach for organ replacement, produced using 3D printing techniques. The primary use of printable organs is in transplantation. Research is currently being conducted on artificial hearts, kidneys, and liver structures, as well as other major organs.
Behind 3D printing, the most differentiating concept is that it is an additive production process. This is fundamentally different from any other conventional production techniques that already exist.
3D printing proves to be an innovative technology that encourages and drives innovation with unparalleled flexibility of design while being a tool-free process that eliminates prohibitive costs and lead times.
3D printing is also emerging as an energy-efficient technology that can provide environmental efficiencies in terms of both the manufacturing process itself, utilizing up to 90% of standard materials, and throughout the product operating life, through lighter and stronger design.
Applications
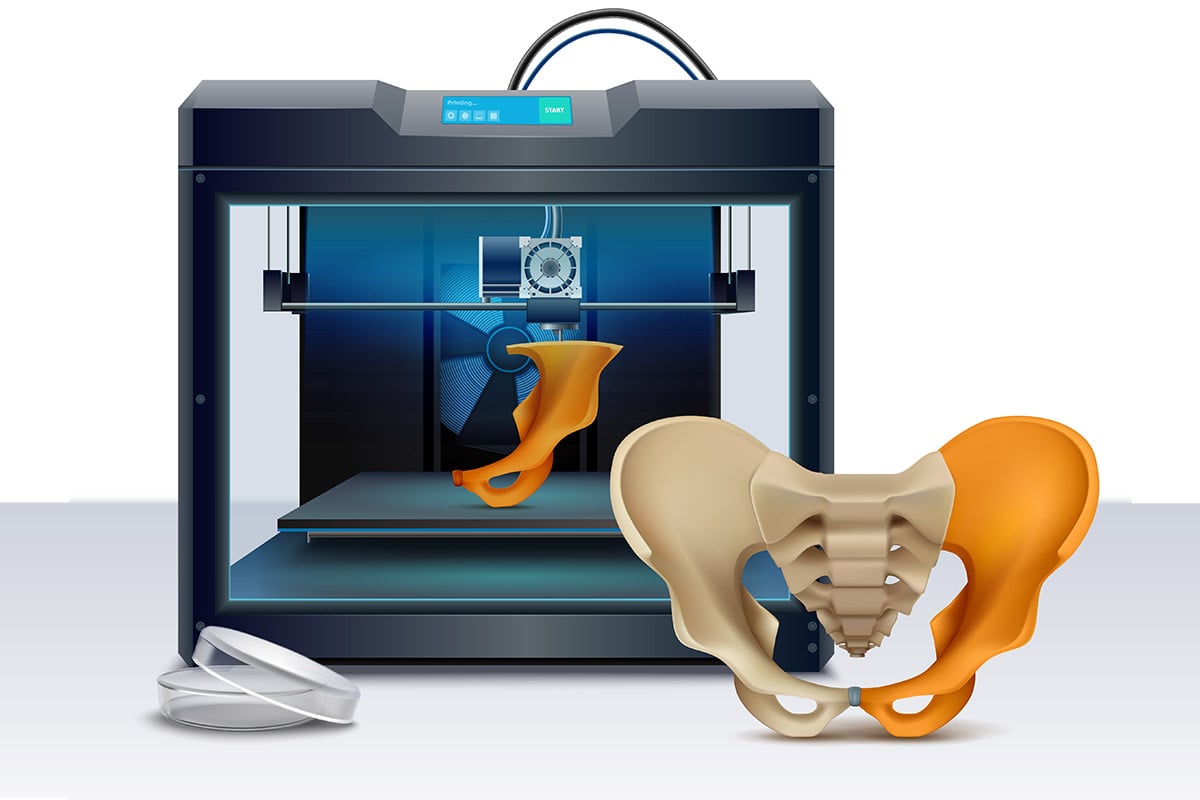

A New Era in Personalized Medicine
Medicine is one of the most popular fields for anything technology, especially 3D printing. The medical field is in store for a lot when it comes to 3D printing organs for the organ shortage in the country, surgical tools, custom-made prosthetics, and the list goes on and on.
3D printing will bring anything from imagination into real life, and medicine is just another field ready for disruption.
3D printing shows immense promise when it comes to stocking up on medical supplies, hip and knee implants, personalized prosthetics, and one-off implants for patients suffering from diseases such as osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, and cancer, along with accident and trauma victims.
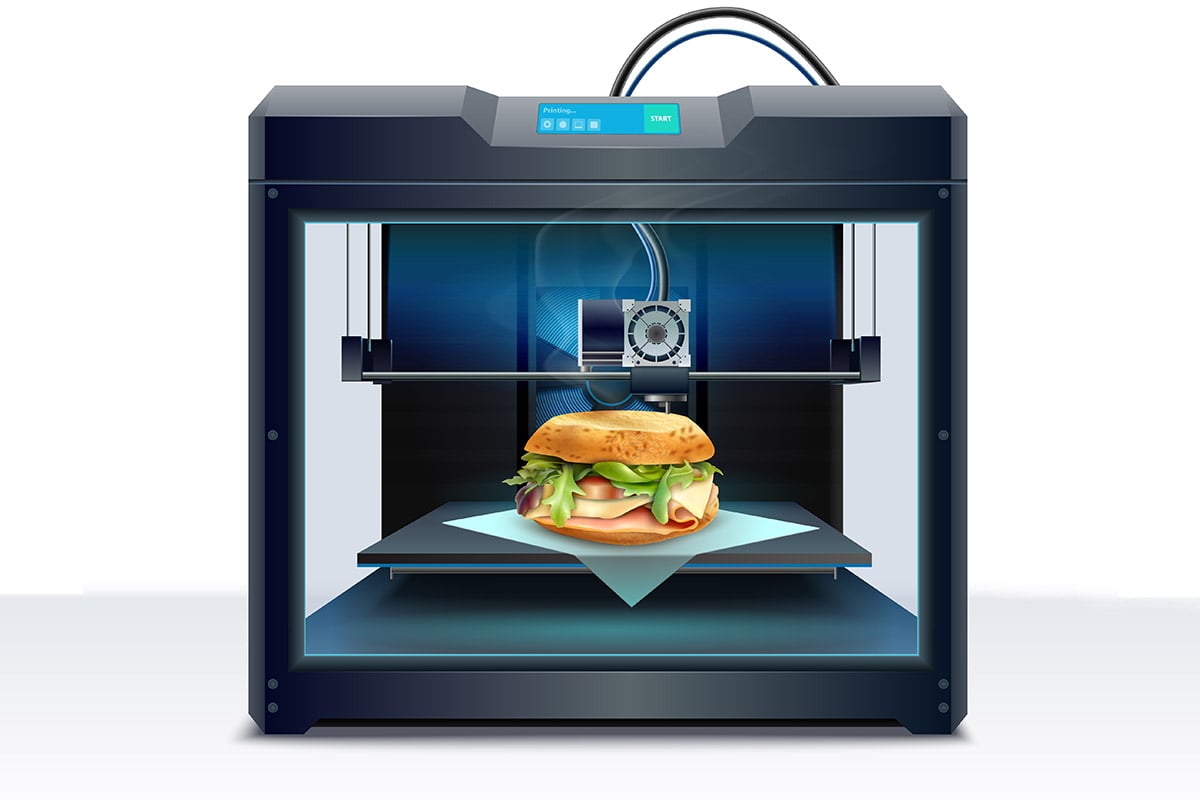

The Food Industry
3D printing is emerging as a new way of preparing and presenting food. For people in developing countries with food shortages, 3D printing is an exciting new innovation on the rise that can help with that cause-maybe even putting a stop to global hunger.
3D printing has already begun for chocolate/sugar, but early experiments with food including the 3D printing of “meat” at the cellular protein level (cellular agriculture & using stem cells to even print food).
The future of 3D printing in food is being used as a way to balance our nutrients in a diet and promotes healthy eating habits for complete food preparation methods.
Aerospace & 3D printing Rockets
The aerospace field is also an industry adopting 3D printing just like the healthcare field, 3D printing crazy parts from satellites to rockets for aircraft use. But 3D manufacturing in space still continues to be a struggle, as it requires new technology to adapt to the space environment and more resistant materials
Inside space stations, this could be incredibly useful if something is broken and is needed to be replaced, 3D printing the parts could solve that problem. A 3D printer working in orbit would be able to create satellite structures that report back to Earth.
Challenges include 3D printing without the use of gravity in space since the printer has no support & has to shape the 3D printed material in the vacuum of space. Resistant material that evolves to space-based conditions proves to be another struggle, but also a problem that has a lot of opportunity for 3D printing. Imagine-what if we could 3D print medical supplies in space next?
Get in touch
Transform your business to the next level.

